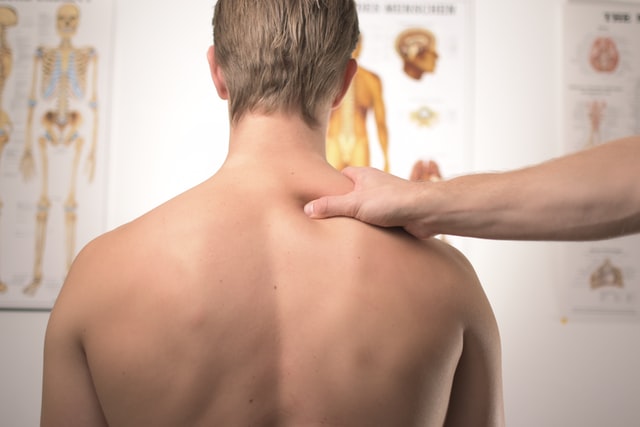
Thoracic discopathy very often affects middle-aged people who spend a lot of time sitting in front of the computer. Other factors leading to thoracic discopathy include excessive physical exertion, mechanical trauma, and changes in bone chemical composition. Chest pain, sensory disturbances, or nausea may be some of the symptoms of this condition. Can herniated disc cause chest pain?
Symptoms of thoracic discopathy
As with cervical or lumbar discopathy, pain often does not occur exactly where the disease has been attacked. With thoracic discopathy, ailments are often not associated with pain in the thoracic region of the spine.
The most common symptoms of thoracic spine discopathy are:
- radiating, local pain, arising from compression of the nerve root that occurs in the lower extremities;
- sensory disturbances, tingling, smoking and pressure in the lower extremities;
- impaired mobility, which is directly related to the disorder of the function of motor fibers, which innervate individual parts of the muscles of the lower extremities;
- in the case of advanced hernia – sudden paralysis of the lower limb muscles;
- strong muscle tension.

What are the causes of an intervertebral disc hernia?
Many factors can lead to the disk falling out. The main causes of thoracic discopathy are similar to those causing hernia of other sections:
- posture defects (associated with diseases of the spine or type of work, e.g. scoliosis, non-physiological thoracic kyphosis, incorrect body posture);
- sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity associated with low mobility of the spine and low stretch of soft tissues, often associated with rapid movement;
- excessive physical exertion associated with overloading the spine;
- spinal injury or intervertebral disc microtraumas;
- back diseases;
- lesions of the intervertebral disc (dehydration, degeneration).
If, due to adverse factors, the changes involve several disks, we are talking about multilevel thoracic discopathy.
It is comforting that thoracic back pain is rare
Many people’s fear of getting discopathy is – rightly – great. We cancel the alarm for discopathy in the thoracic spine: disc prolapse in the thoracic spine plays only a minimal role compared to the occurrence of discopathy in the cervical spine (C) and lumbar (L). In figures: only 2% of all disk-related diseases affect the thoracic spine.